The Middle East, an area rich in oil fields, is rapidly becoming a game changer in the world of artificial intelligence (AI). This may come as a surprise to some, especially considering the region’s long-standing interest in energy. But recently, countries in the Middle East have begun to take significant steps towards leading in AI technology. Although this change is happening rapidly, many people, including business leaders, investors, and even policymakers, are wondering what is driving this change.
The information about AI in the Middle East is often ambiguous or incomplete, making it difficult to comprehend. What is real and what is just talk of the progress? There are numerous countries in the region investing in AI, making it challenging to determine what is truly happening. This confusion makes it hard for those interested in the Middle East’s tech growth to view the bigger picture.
This article aims to clarify matters. We will examine some of the key factors that will enable the Middle East to develop as an AI leader. We will cover the plans, technology, people, and industries where AI is truly changing the world. By the end of this article, you will be able to gain better insight into how the Middle East is lighting up the future of AI.
| Country | Key AI Initiatives/Strategies | Major Investment Areas | Progress/Milestones |
| Saudi Arabia | National Strategy for Data & AI (NSDAI), NEOM, Red Sea Project, Diriyah Gate | Smart Cities, Tourism, Energy, Finance, Government Services | Launched AI training programs, and significant infrastructure projects are underway |
UAE | National AI Strategy 2031, UAE Centennial 2071, G42, Dubai AI Roadmap | Smart Cities, Government Services, Healthcare, Logistics, Finance | Established first Ministry of AI, major investments in AI companies globally |
Qatar | National AI Strategy, Qatar Foundation, Smart Qatar Program | Smart Cities, Healthcare, Education, Sports | Significant R&D investment, focus on specific application areas (e.g., healthcare during COVID-19) |
| Israel | National AI Program, Innovation Authority | Cybersecurity, FinTech, HealthTech, Autonomous Vehicles | High density of AI startups, strong academic research, significant VC funding |
Key Drivers Fueling the Middle East’s AI Ambitions
1. Government Vision & Support
Like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Qatar, Middle Eastern governments have set AI at the top of their national plans. This clear vision from the leaders means that AI is not just a trend but also a long-term strategy with serious endorsement and clear objectives. To see how the region is preparing for upcoming tech showcases like the GITEX Global Preview, Future of Generative AI, explore the latest innovations shaping AI in the Middle East.

2. Wealth from Oil
The region’s oil wealth has enabled governments to invest heavily in AI. Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) are utilised to finance AI projects, attract talent, and develop infrastructure to support AI development across various industries.
3. Moving Away from Oil
Middle Eastern countries view AI as the catalyst for new industrial enterprises based on technology. AI is facilitating the development of key areas such as finance, health, and logistics that are essential to their plan of economic diversification.
4. Young and Digital-First Population
The Middle East has a technologically brilliant youth that is willing to learn new skills. This group is a potentially employable one for AI jobs and a market for AI-powered services and products.
5. Strategic Location
The Middle East is a crucial hub for the world, particularly in terms of trade and data, situated between Europe, Asia & Africa. AI is being used to improve logistics, connectivity, and trade in this region of strategic importance.
6. Global Influence
AI is being utilised by countries in the Middle East to enhance their global influence. With the development of AI technologies, they plan on playing a bigger part in international technology discussions and innovations.
Building the Foundation: Infrastructure Development
1. Data Centres
Data centres are crucial for the storage and processing of the vast amount of data required to run AI models. The Middle East is seeing massive investments in hyperscale data centres by both global tech companies and local players.
2. High-Speed Connectivity
AI needs high-speed and reliable internet for fast data transmission to support real-time applications such as smart cities and self-driving cars. Countries in the Middle East are rapidly deploying 5G networks to ensure that cities and businesses have the necessary connectivity to support the smooth operation of AI systems.
3. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing allows businesses to access computing resources on demand without needing significant investments. The Middle East is partnering with global cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud in order to have a local presence and deliver scalable AI solutions to businesses.
4. Fibre Optics and Network Upgrades
The efficient functioning of AI requires a fast and stable internet connection. The Middle East is spending money expanding and modernising fibre-optic networks to be able to accommodate the vast amounts of data needed for AI applications. This will enhance the overall network speed and capacity throughout the region.
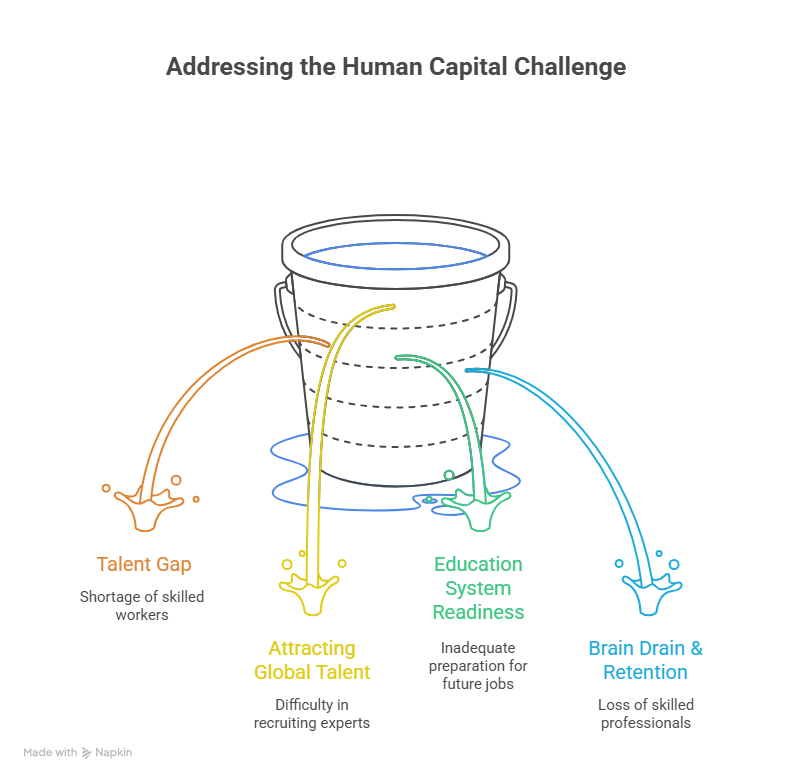
The Human Capital Challenge: Talent and Education
A lack of a skilled workforce is one of the significant challenges that the Middle East must overcome in building its AI business. Although the region has big plans for AI, there is a need for more professionals to be trained for AI jobs. This is how the Middle East is solving this problem:
1. Talent Gap
Many countries are opening specialised AI universities and training programs in order to grow a strong AI workforce. There are also partnerships with global institutions and national training initiatives. Nevertheless, there is still a large gap of skilled workers to be filled.
2. Attracting Global Talent
The Middle East is not only offering competitive salaries long long-term visas but also attractive living arrangements for global AI talents. This plays a part in attracting seasoned researchers, engineers, and innovators to strengthen the region’s AI ecosystem and create more jobs locally.
3. Education System Readiness
Several nations are attempting to integrate AI and data science into their school curricula and train teachers to teach these topics. The objective is to train the younger generation in digital literacy and a basic understanding of AI, so that future generations will be equipped to tackle AI challenges.
4. Brain Drain & Retention
To retain the best local talent, countries are creating more career opportunities in tech and AI. They are also encouraging expatriates to stay by providing funding for research and a dynamic tech ecosystem. This will help retain top talent and develop local AI expertise.
AI in Action: Key Sectors and Applications
AI is already having a significant impact in various sectors across the Middle East. Countries in the region utilise the AI technologies in solving tangible issues and to enhance efficiency and innovation in their respective areas. Below are some of the key sectors currently actively being used by AI:
1. AI in Energy (Oil/Gas/Renewables)
AI is revolutionising the Middle East’s energy sector. Using AI-powered tools for predictive maintenance enables firms to avoid equipment failures and minimise expenses. Moreover, AI is applied in reservoir optimisation for oil and gas production and in the control of smart grids for renewable energy, such as solar. AI helps Aramco, the region’s largest oil firm, to increase efficiency in exploration and production.
2. AI in Finance (FinTech)
The financial sector in the Middle East is adopting AI to deliver improved services. AI algorithms are being applied to fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and customer service chatbots. AI-powered personalised banking services are also becoming widespread, which helps the banks to provide customers with customised financial advice and products. Places such as Dubai and Riyadh are becoming FinTech hubs, and cities are quickly growing as such, where AI is revolutionising how people manage their money.
3. AI in Healthcare
AI is aiding in enhancing healthcare services in the Middle East. Medical imaging analysis and AI-powered diagnostics are helping doctors provide quicker and more accurate diagnoses. Personalised medicine that customises treatment plans according to individual patients is also a use of AI. The use of AI in delivering telemedicine is increasing and is a bigger mode of providing healthcare in remote areas.
4. AI in Smart Cities
Smart cities are among the most innovative AI applications in the Middle East. AI is harnessed to control traffic, enhance waste management, and promote energy efficiency in cities. NEOM, a futuristic city in Saudi Arabia, is starting from the ground up in integrating AI into daily life.
5. AI in Tourism & Hospitality
The tourism and hospitality industries are leveraging AI to enhance customer experiences. AI-powered personalised recommendations and automated guest services are making travel convenient and fun. Dynamic pricing systems utilise artificial intelligence to adjust prices based on demand, ensuring effective pricing strategies for hotels and airlines.
6. AI in Logistics & Transportation
AI is making logistics and transportation more intelligent. AI-driven supply chain optimisation assists companies in maintaining their inventory and shipments better. Self-driving cars and drones are being experimented with for deliveries and transportation. The UAE’s Jebel Ali Port has already integrated AI-driven automation to improve port operations.
Navigating the Hurdles: Challenges and Roadblocks
Although the Middle East is already making significant progress with AI, several challenges still need to be addressed. These are hurdles, which include regulatory, data privacy, and long-term sustainability considerations. Let’s examine the significant challenges the region faces on its path to AI development and explore possible solutions for them.
1. Regulatory Frameworks
AI development in the Middle East is constrained by the presence of nascent or confusing regulations on the deployment of AI, the use of data, and ethics. Governments are developing AI ethics guidelines and rules to ensure responsible AI usage.
2. Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are key concerns with AI, particularly when it involves large volumes of data. There are concerns about how personal data is managed and protected. To address such problems, the Middle East is drafting a robust data protection law, similar to the GDPR in Europe. Besides, there is an increasing investment in cybersecurity to protect sensitive information from possible leaks.
3. Cultural Adaptation & Trust
In some sectors, or among the public in the Middle East, there may be reluctance to fully embrace AI, especially in areas such as healthcare or government services. Societies need to trust AI systems, and numerous government initiatives focus on educating people about the benefits of AI. Community involvement in the design and use of AI technologies can also contribute to a more positive perception of AI.
4. Long-Term Sustainability
The development of AI requires more than just government investment; it also needs continuous innovation from both the public and private sectors. Countries in the Middle East are working to create vibrant startup ecosystems and encourage venture capital growth to support long-term AI company development.
5. Hype vs. Reality
There is a lot of excitement surrounding AI in the Middle East, and it is especially important to differentiate between ambitious announcements and actual large-scale implementations. Governments and companies are focusing on measurable results and transparent reporting to ensure that AI projects deliver tangible outcomes. Pilot projects and critical assessments are providing insights to distinguish hype from reality.
6. Data Access and Quality
Higher-quality data is essential for the training and operational success of AI systems; however, most countries in the region face challenges with data access and quality. To overcome this hurdle, governments and firms are working to develop data-sharing frameworks with robust privacy guardrails. Additionally, investing in data labelling and curation should be considered to enhance the quality and reliability of the data.
Case Study Deep Dive
To understand how AI is being introduced in the Middle East, one of the best ways to gain insight is to examine specific projects or countries that are at the forefront. Let’s talk about NEOM, a future-oriented city in Saudi Arabia, and how AI is shaping the future of the area.
NEOM: A Smart City Powered by AI
NEOM is the ambitious mega-project that Saudi Arabia has initiated as part of their Vision 2030. The city is being developed at the ground level to become a world centre of innovation, sustainability, and AI technology. The project differs in its approach to city planning, utilising AI-powered systems that manage everything, from transportation to energy usage.
In addition to its technological innovations, NEOM is designed to be a model for sustainability, utilising AI to efficiently manage natural resources, reduce waste, and promote clean energy solutions. The project also emphasises the top-down aspiration of Saudi Arabia to digitise AI from urban planning to environmental management across the infrastructure.

Future Outlook and Global Implications
1. Increased Global Competition
As the Middle East advances in AI, it will compete with established tech hubs like Silicon Valley and Beijing for talent, investment, and influence. To stay competitive, the region will need to focus on specific niches where it has a natural advantage, such as smart cities, energy management, and healthcare innovation.
2. Regional Collaboration
While there is competition, the Middle East also has the potential for increased AI collaboration among countries within the region. Exchanging data, research, and best practices can accelerate progress and foster a more substantial regional bloc. Political intricacies will be vital, but regional cooperation could unite the Middle East as a single voice in the global AI race.
3. Ethical & Governance Leadership
The Middle East is well-positioned to shape global conversations on AI ethics and governance, particularly from a non-Western perspective. The region can develop AI ethics frameworks that consider local cultural values and international best practices. If success is achieved, the Middle East could become a leader in AI governance, making its mark on global AI usage.
4. Investment Flows
With continued investment in AI by the Middle East, the region is poised to emerge as a key hub for global AI companies. Meanwhile, the foreign investment in the AI sector of the Middle East is expected to rise. This opens up an opportunity for both domestic and international players to collaborate and accelerate innovation, ultimately bringing more AI solutions to market.
5. Addressing Regional Challenges
AI can also support the solution of certain distinctive Middle East problems, such as water scarcity and solar energy efficiency, or even desert agriculture. By applying AI to develop cutting-edge solutions to such challenges, the Middle East can not only transform the lives of its own citizens but also establish an international footprint by addressing complex, real-world problems.
Conclusion
The Middle East is on a fast track to becoming a global leader in artificial intelligence, driven by government vision, strategic investments, and a strong push to diversify its economy. Whether it is massive infrastructural projects, such as NEOM, or regional partnership deals, or the rise of AI in key fields like energy, healthcare, or finance, the region is on its way to becoming a significant player in the AI revolution.
Major enablers, such as the region’s wealth from oil, its young and digitally savvy population, and a clear commitment from national governments, are setting the perfect conditions for AI to thrive. At the same time, issues such as data privacy, talent gaps, and regulatory frameworks must be addressed for the growth of AI to be sustainable. The Middle East is not only restructuring its economy but is also attempting to shape the global AI landscape.
In the coming years, the Middle East is likely to become a key hub for AI innovation and application, with the potential to shift the global balance of technological power. The future of AI in the region appears promising, and its impact will be felt globally.




















Leave a Reply