Have you ever wondered what all the hype about artificial intelligence (AI) is all about on the news, in social media, and in every conversation that you participate in? Terms such as the “machine learning,” “neural networks,” and “deep learning” appear everywhere but are usually explained in a way that confuses or overwhelms most people. The technical jargon may be intimidating, especially if all you want is a basic peek into the latest trends in tech.
However, the truth is that understanding AI need not be complex. In today’s world, basic knowledge of AI is becoming increasingly important, whether for personal interest, professional development, or simply to stay current with the technologies that shape our lives.
This guide aims to simplify the complexity of explaining AI terms by breaking them down into clear, easy-to-understand descriptions. If you are new to AI or would like to refresh your understanding of AI basics, this guide will provide clarity on AI terms and their impact on your world. Let’s get started!
Demystifying Core AI Concepts: A Beginner’s Glossary
In this part, we are going to break down some of the most fundamental AI terms that you will encounter. To most people, AI may seem like a foreign concept when first heard, but through our explanations in simple, everyday language, we hope to make it easier for you to understand. We will use relatable analogies and examples that will associate those terms with things that you are already familiar with, so you won’t just learn what they mean but how they function in real life.
The focus in this case is to provide you with an understanding of the building blocks of AI. We will review the main idea, clarify its meaning, and illustrate how it all works together to make AI operate. Therefore, even if you have heard them before or you are hearing them for the first time, by the end of this section, you will feel more comfortable and confident in understanding the basics of AI.
We will also make sure to focus on those terms that are crucial to comprehending the modern AI applications that you’re likely to run into every day, be it your phone’s voice assistant or a recommendation engine on your favorite shopping site.
Breaking Down AI Terms with Simple Analogies
Now that we have set the stage, let’s dig into each key AI term in terms that are easy to understand. We’re going to make things easy for you by utilising everyday language and analogies that relate these terms to what you already know. By the end of this section, you will learn much more about what these terms mean and where they belong in the greater context of AI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Definition: AI is about enabling computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding speech, acting autonomously, and recognising objects.
- Analogy: Imagine designing an intelligent robot that can think and decide like a person (yet much faster!). It can be influenced by experience and improve in the same way we do.
Machine Learning (ML)
- Definition: ML is a technique that allows computers to learn from data without the need for programming. They become better with the increasing data.
- Analogy: It is similar to teaching a child to recognise animals by showing many pictures until that child notices the patterns. The more examples they watch, the better they become at identifying animals by themselves.
Deep Learning (DL)
- Definition: Deep Learning is one of the Machine Learning types that utilises complex multi-layered networks (called neural networks) to uncover patterns in data.
- Analogy: Think of peeling an onion. Every layer of the onion allows seeing further insights. Likewise, deep learning is based on layers of data to explore more detailed and accurate information.
Neural Network
- Definition: A Neural network is a structure based on the human brain where information is processed by interconnected units called “nodes”.
- Analogy: Think of a system of switches for light. Turning one on can cause others to shine. In a neural network, engaging one node affects others, enabling the system to process complex information more effectively.
Supervised Learning
- Definition: Supervised Learning is when a computer learns from labelled data—examples that already have the correct answer attached.
- Analogy: It is like having a teacher who teaches you a math problem and then tells you the correct answer. In the long run, the computer becomes capable of addressing similar problems independently.
Unsupervised Learning
- Definition: Unsupervised Learning is a process where a computer identifies trends in data on its own, without being explicitly instructed on how to do so.
- Analogy: Pretend you receive a large assortment of toys in a mess and are asked to sort them. You do it by seeing resemblances, such as placing all cars together and all dolls in another group, without anyone’s instructions.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Definition: NLP is a branch of AI that enables computers to understand and respond to human language with ease.
- Analogy: It is like teaching a computer to read and speak to you, just like how Google Translate converts one language word to another.
Computer Vision
- Definition: Computer Vision enables computers to perceive and comprehend the world through the images or videos they receive.
- Analogy: Think about teaching a computer to identify objects in pictures or videos, for example, a cat or a car. It is like helping the laptop “see” and understand the world around it.
Algorithm
- Definition: An algorithm is a sequence of step-by-step instructions that tells your computer how to solve a real problem.
- Analogy: It is like a recipe. Just as a recipe guides you in cooking a meal, an algorithm guides the computer in solving a problem.
Data Set
- Definition: A dataset refers to a group of data used to train or test an AI system.
- Analogy: Just imagine a photo album with pictures of cats and dogs in it. With this data set, the computer learns the difference between the two and how to recognise them.
How AI Works in Real Life: Everyday Examples You’ll Recognise
If you’re curious about how these terms apply in real tools, check out our guides on ChatGPT for Content Writing and the visual comparison Midjourney vs. DALL·E. After hearing the definitions and analogies behind each term, the real thing now comes into focus; we need to see the actual working of these AI concepts in the real world. Let’s review some real examples of the use of these AI notions in action:
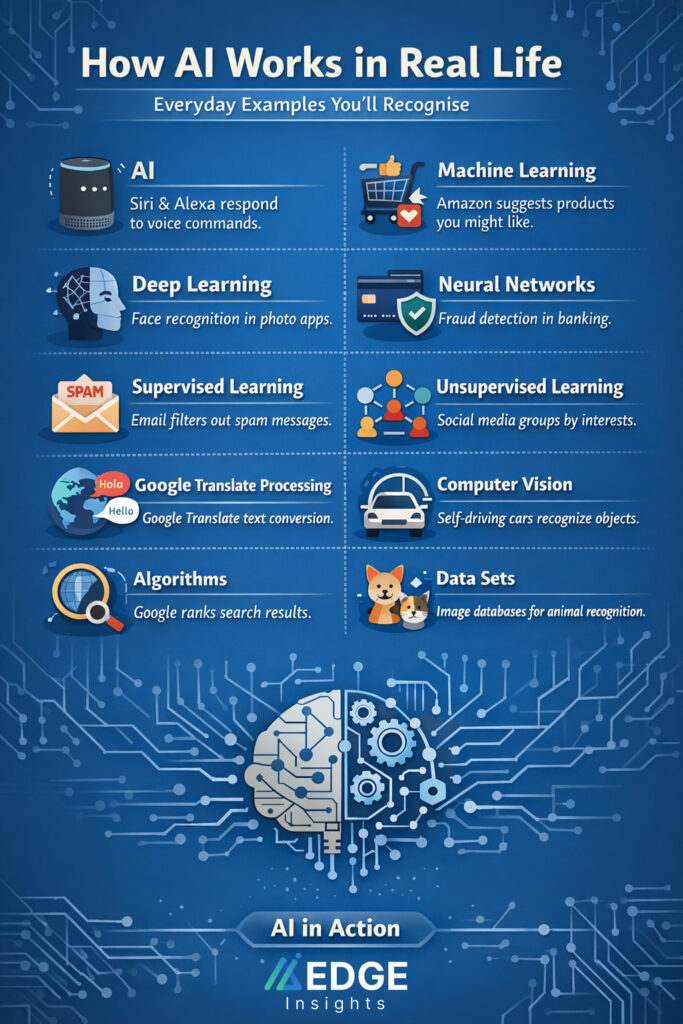
1- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence is utilised in virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to comprehend and respond to voice commands. Whether asking for the weather or playing a song, these assistants are leveraging AI to understand your voice and determine the action to take.
2- Machine Learning (ML)
Products are recommended to you by online shopping sites such as Amazon based on your previous purchases and browsing patterns. These recommendations are driven by machine learning algorithms that learn more about your tastes as they go on and predict what else you might be interested in.
3- Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning is applied in facial recognition systems, such as those used in your smartphone’s photo gallery. When you tag someone’s face, the machine is expected to recognise and identify the individual in other images as it improves with time when processing more information.
4- Neural Network
Neural networks are commonly applied in financial services to detect fraudulent credit card transactions. Such networks examine trends within transaction data and report any suspicious activity by analysing the trends over historical data.
5- Supervised Learning
Email spam filters learn through the process of supervised learning. They learn to recognise spam messages by seeing both spam and non-spam messages. Over time, they become more effective at selecting unwanted emails using this tagged information.
6- Unsupervised Learning
Social media platforms apply the unsupervised learning technique to divide users into groups depending on their interests and behaviours. For example, Facebook might group users who engage with similar types of posts, even if it wasn’t explicitly told to do so.
7- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Google Translate applies NLP to convert text from one language to another automatically. It knows the structure and context of your words, and for this reason, it will produce a meaningful translation that flows well in the target language.
8- Computer Vision
Self-driving cars rely on computer vision to move on the streets. They utilise cameras and sensors to detect pedestrians, other vehicles, traffic signs, and obstacles, enabling the car to see and make driving decisions without human input.
9- Algorithm
Search engines like Google use complex algorithms for ranking web pages according to their relevance to the search query. These algorithms consider various factors, including the use of keywords, content quality, and user experience, to determine which page should appear first.
10- Data Set
AI models trained to recognise animals in photos utilise large datasets of labelled images. For example, a data set might contain thousands of pictures of cats and dogs, allowing the AI system to learn to distinguish between the two and identify them in new images.
How All These AI Terms Fit Together: The Bigger Picture
Technologies like deep learning, neural networks, and datasets all work together behind the scenes to power many AI tools, especially those that create images. If you want to explore how AI helps tools like these turn text into art, check out Midjourney vs. DALL-E for Designers: The Ultimate Comparison. Here, we will discuss how the primary terms of the AI we have addressed are interconnected.
Knowing the connections will enable you to understand how various aspects of AI work together to create the technology we use today. Let’s break it down:
AI as the Umbrella
An umbrella term encompasses all methods and techniques used to make machines “smart.” Artificial Intelligence encompasses various technologies, including Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and more specialised areas such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision.
Machine Learning (ML)
Considering ML, this is a part of AI. It is one way to teach machines how to learn from data. Although AI is a general concept, ML is the specific study of learning algorithms that improve with experience.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning is another subset of ML, and it’s the one that emulates the work of the human brain through its multi-layered neural networks. While ML is focused on learning from the data in general, DL works deeper and solves more complex issues by analysing the data through several layers.
How Machine Learning and Deep Learning Relate
Neural Networks
They are a fundamental aspect of ML and DL. In ML, a neural network can be applied to solve a problem as patterns are looked for in the data. In DL, the neural networks become more and more layered as more advanced information is processed.
Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
These are the forms of learning in ML. Supervised learning refers to an algorithm that learns from data containing labelled examples, whereas unsupervised learning allows the machine to discover patterns in data with no predefined labels. Machines in data processing utilise both types of learning, but in distinct ways.
AI Applications
AI’s real-world applications are where the individual concepts shine. For instance, Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables computers to comprehend and produce human language, which is crucial in areas such as voice assistants and language translation services. Computer Vision, in turn, enables machines to “see” and comprehend visual data, which is crucial for applications such as self-driving cars and image recognition apps.
Busting AI Myths: What’s Real and What’s Just Sci-Fi
As AI continues to grow and develop, more misconceptions emerge, making it seem scarier or more confusing than it is. In this section, we will discuss some common myths about AI and provide the reality behind these misconceptions. This will be useful in differentiating fact from fiction, making it easier to understand how AI actually works.
AI is Always Right (Fiction vs. Facts)
- Myth: Many people believe that AI systems are infallible and always make the right decision. Whether it is a recommendation engine, a voice assistant, or a self-driving car, it is common to assume that AI is always perfect.
- Reality: In fact, AI is only as strong as the data it has been trained on. The AI’s decisions can also be faulty when the data is biased or incomplete. For instance, a hiring system empowered by AI may discriminate against certain groups of people unintentionally if it is trained on biased historical data. AI also has its flaws, as it can misinterpret spoken words or confuse objects in an image. It is essential to note that, although AI can be highly accurate, it is not always perfect.
AI Can Think Like Humans (Myth vs. Reality)
- Myth: Another common misconception is that AI can think and reason like humans. Many individuals believe that AI can comprehend emotional context and make decisions that humans do.
- Reality: Although AI can be used to mimic human-like behaviour to an extent, it does not “think” or “feel” like a human. AI works on algorithms and patterns developed from the data. It lacks consciousness, emotions, and knowledge of the real world. For instance, a chatbot might be empathetic to you, but it is only using pre-programmed rules, and it does not feel emotions.
AI Will Take Over All Jobs- (Myth vs. Reality)
- Myth: People are afraid that AI will replace all human jobs, leaving everyone unemployed.
- Reality: Although AI undoubtedly automates various tasks, especially repetitive and data-intensive tasks, it is unlikely to eliminate all jobs. Instead, AI will alter the nature of work. AI will complement many jobs, and people will work together with AI tools to enhance efficiency and productivity. For instance, doctors may use AI to analyse medical images faster, but they will still give the final diagnosis. AI is a tool used by humans, not a replacement for humans.
AI Knows All (Myth and Reality)
- Myth: People believe that AI understands everything in depth, like complicated issues and abstract ideas.
- Reality: AI does not really “understand” anything in the sense of humans. It analyses data, learns patterns, and makes predictions, but does not understand the information like humans. For instance, although AI can translate languages, it may not pick up the subtle meanings or context that a human translator would grasp easily.
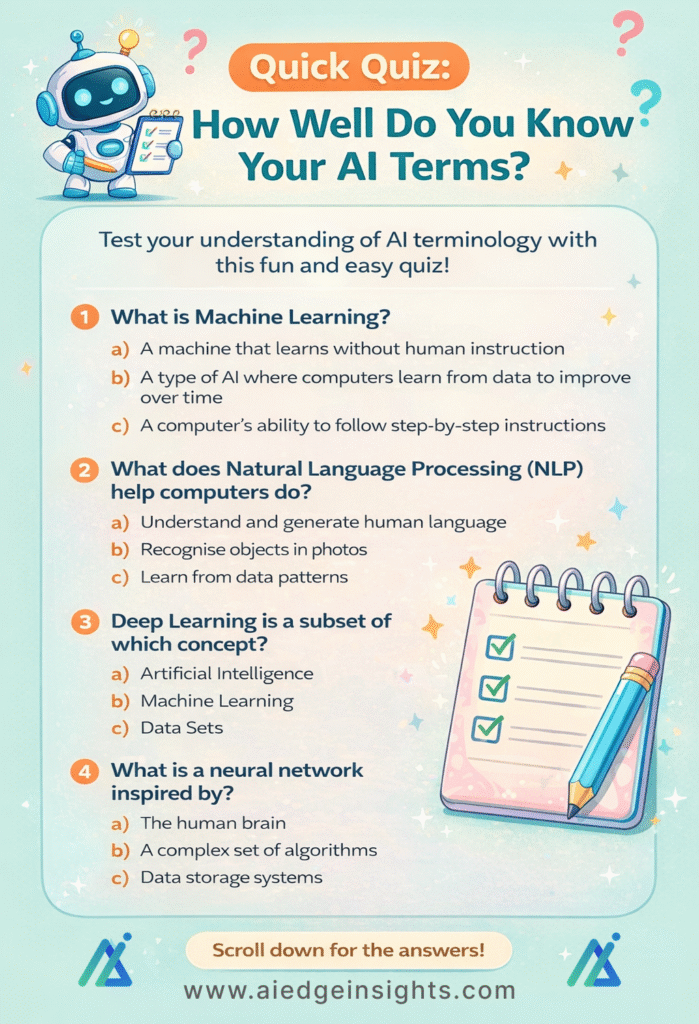
Quick Quiz: How Well Do You Know Your AI Terms?
Now that we’ve covered the basics of AI terminology, it’s time for a quick, fun quiz to test your understanding! This quiz will help you review what you have learned so far and make sure you’re comfortable with the key concepts. Don’t worry—it’s meant to be enjoyable and straightforward!
1. What is Machine Learning?
a) A machine that learns without human instruction
b) A type of AI where computers learn from data to improve over time
c) A computer’s ability to follow step-by-step instructions
2. What does Natural Language Processing (NLP) help computers do?
a) Understand and generate human language
b) Recognise objects in photos
c) Learn from data patterns
3. Deep Learning is a subset of which concept?
a) Artificial Intelligence
b) Machine Learning
c) Data Sets
4. What is a neural network inspired by?
a) The human brain
b) A complex set of algorithms
c) Data storage systems
Next Steps: Learn More About AI with These Easy Resources
Now that you know the fundamentals of AI terminology, it is time to dig deeper and carry out further learning. AI is a huge area, and there is always more to discover. Below are some useful resources and tips to help you get more educated and informed about the latest news on AI.
1. Beginner-Friendly Online Courses
- Coursera – “AI for Everyone”: This course, taught by Andrew Ng, one of the pioneers of AI, is best for beginners. It presents the AI concepts in a human-friendly manner, emphasising what AI can and cannot do.
- edX – “Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)”: Provided by Microsoft, this course explores fundamental AI concepts and their real-life implementations.
These courses are instrumental in acquiring a structured knowledge of AI, and they provide a pace of learning.
2. Well-respected tech News Sections on AI
- MIT Technology Review – AI Section: Read the latest AI breakthroughs and industry news. MIT’s AI section provides insights into the various ways AI is being applied in different areas.
- Wired – Artificial Intelligence: Wired regularly publishes articles on AI, from beginner-level pieces to advanced topics. It is a perfect way to get up to date with new trends and difficulties in the field.
3. Glossaries from Trusted Academic/Research Institutions
- Stanford AI Index: Stanford’s AI Index is a valuable resource that provides research, papers, and glossaries on the latest AI technologies.
- Google AI Glossary: Google offers an easy-to-understand AI glossary covering a range of terms, from basic concepts to more technical ones.
4. Visual Learning Platforms
- YouTube Channels: Platforms such as “3Blue1Brown” and “CrashCourse” provide outstanding, visually appealing explanations of AI concepts, utilising animations to make complex concepts easier to understand.
- AI Demos and Interactive Simulators: Sites such as Teachable Machine by Google allow trying hands-on AI experiments like training a model to recognise objects, sounds, or even poses. This interactive learning strategy can help you understand AI by providing practical experience.
5. Books for Further Reading
- “Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans” by Melanie Mitchell: In this guide, you will find a complete and accessible overview of AI history, how it works, and where and to what extent it can be applied. It’s ideal for anyone who wants to delve deeper into AI, beyond the basics.
- “Deep Learning” by Ian Goodfellow: For those eager to learn about machine learning and deep learning, this book by one of the leading specialists in this industry is highly recommended.
Why These Resources Are Helpful:
- Structured Learning: Internet courses and books help individuals learn AI concepts in a step-by-step manner.
- Staying Updated: Tech news sites, such as MIT Technology Review and Wired, keep you informed about the latest and world-applicable AI developments.
- Interactive Experience: Interactive demos and simulators allow you to put into practice what you’ve learned, giving you practical experience working with AI models and concepts.
- Visual Learning: YouTube channels and visual education resources help individuals understand complex concepts through the use of attractive images and clear descriptions.
Conclusion
Learning about artificial intelligence does not have to be difficult. By simply being aided and making sense of explanations, you can master the world of AI without falling into the jargon. In this guide, we have simplified important terms – including machine learning, deep learning, neural networks, and a few other concepts – using simple words, analogies, and real-life examples to make each concept learner-friendly.
By learning these terms, you’ve taken a big step toward understanding how AI shapes the technology we use every day—from virtual assistants and recommendation systems to self-driving cars and language translators. Now, you have a basis that can help you stay up to date with conversations about AI, try out new tools, and even dive into further learning if you feel so. The world of AI, which was once so confusing, is now far more familiar.
You can take a step further by maintaining curiosity. Discover what we have shared — watch videos, play some interactive demos, or take a beginner-level course. Most importantly, do not be afraid to discuss these terms with others or relate them to the things you encounter in your everyday life. The more you immerse yourself in these ideas, the more confident you will be. You have just unlocked the first door to understanding the future—keep going, and enjoy the journey ahead!



















Leave a Reply